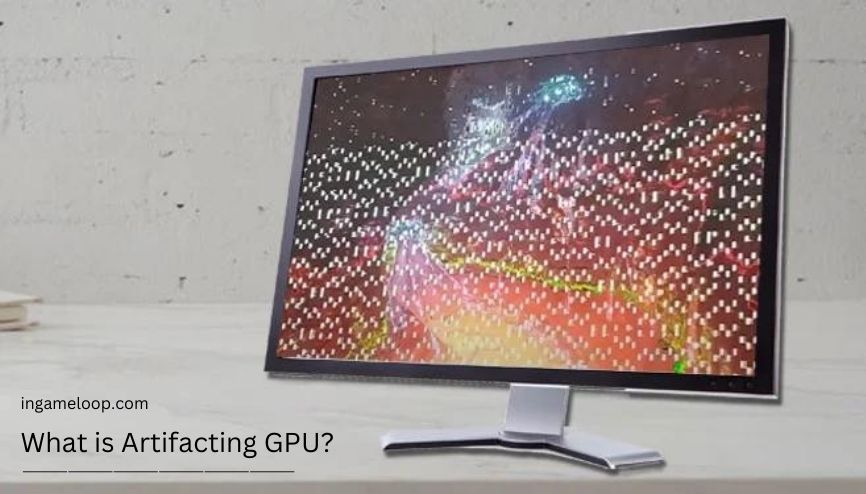

The word Artifacting refers to the graphic defects caused by inaccuracies in the GPU’s calculation. Sometimes a graphics card is unable to properly do some computations, so you may see some unusual graphics affect on the monitor while playing games—this is known as GPU Artifacting. For better understanding, suppose your GPU was producing an automobile scenario that rendered the car a bright, flat pink instead of the actual shade of pink. In a video game, Artifacting is the display of pixels that are not part of the original item.
For your information, there may be several outcomes of Artifacting GPU. For example, some random lines, dots, color effects, or screen distortions may occur when Artificating is taking place. All types of such unusual graphics errors are considered under the umbrella of this phenomenon. Let’s explore each Artificating possibility with pictorial examples!
Key Takeaways
- GPU artifacting is a visual glitch that occurs when the graphics card renders corrupted or distorted images on the screen.
- GPU artifacting can be caused by various factors, such as overheating, overclocking, driver issues, faulty hardware, or power supply problems.
- GPU artifacting can damage the graphics card and affect the gaming experience, so users should fix it as soon as possible.
- There are several ways to fix GPU artifacting, such as updating drivers, lowering settings, cooling the system, replacing components, or contacting support.
- Preventing GPU artifacting is better than fixing it, so users should monitor the temperature, voltage, and performance of their graphics cards regularly.
GPU Artifacts Examples
1. Random lines
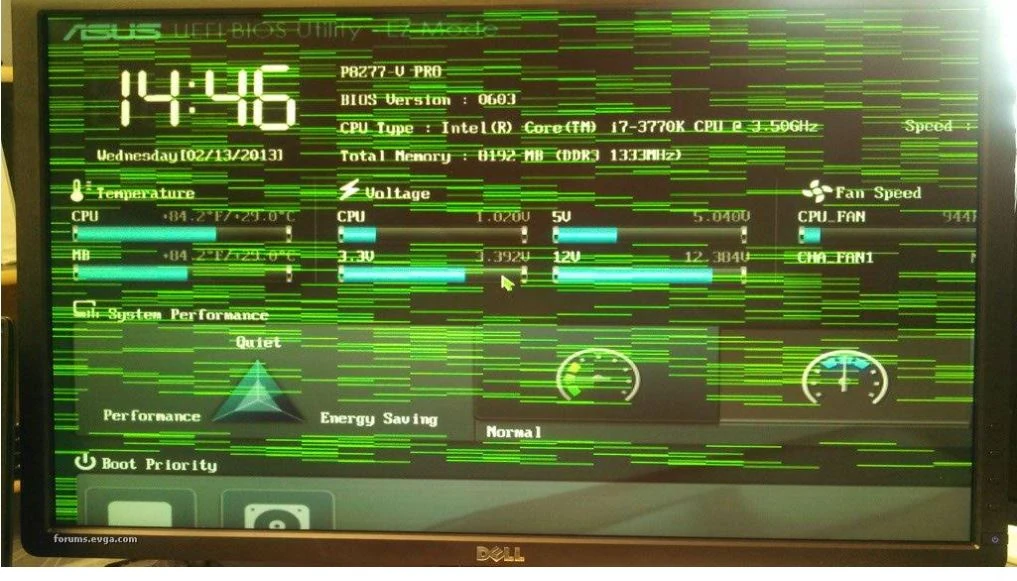
2. Lightning Effects

3. Lightning Effect + Symbols

4. Random Dots

What Causes GPU Artifacting
The causes of GPU artifacting are often multifaceted and can range from hardware issues such as overheating and insufficient power supply, to software problems including outdated drivers or issues with the game or application itself.
Insufficient cooling
A few critical factors can contribute to GPU overheating, which in turn may result in artifacts. First, an inadequate case fan setup can cause issues. Without sufficient case fans, or with an improper fan configuration, airflow within the computer case may be insufficient, leading to heat being trapped and consequently, the GPU overheating.
Second, airflow can also be obstructed by elements like cables, dust, or improperly mounted components. These obstructions can hinder the circulation of cool air within the case, resulting in an increase in internal temperatures.
The third potential cause involves the cooling solutions themselves. Factory-supplied or stock cooling solutions may not always offer optimal performance, and outdated cooling methods may fail to meet the demands of modern, high-performance GPUs. Upgrading to more efficient, aftermarket coolers can significantly enhance cooling capacity, helping to prevent the GPU from overheating.
Lastly, the GPU fans themselves can contribute to the issue. If the fans are broken or faulty, they can’t provide the necessary cooling for the GPU, leading to overheating. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent GPU artifacting and ensure a smoother computing experience.
Dust buildup
One of the common culprits behind GPU overheating and subsequent artifacting is dust accumulation. Specifically, clogged heatsinks due to dust buildup can become less efficient in cooling the GPU, which in turn leads to increased GPU temperatures. Similarly, dust can also collect on the blades of GPU fans, decreasing their performance and impacting the overall cooling efficiency.
This accumulated dust on the cooling components can further impede the system’s ability to dissipate heat. When the cooling system cannot efficiently dissipate heat due to dust buildup, the GPU may overheat, impacting its performance and potentially leading to artifacting.
The cumulative effect of this inefficient cooling and reduced heat dissipation is an increase in GPU temperatures. When temperatures rise above optimal levels, the risk of artifacting increases. Maintaining a clean, dust-free environment inside your computer case is thus crucial to ensuring optimal GPU performance and preventing issues such as artifacting.
Manufacturing defects
Certain manufacturing issues can also contribute to GPU artifacting. For instance, inadequate soldering on GPU components can lead to instability, which can cause artifacting. Unfortunately, diagnosing such issues can be challenging and may necessitate professional assistance, or in some cases, a complete GPU replacement.
Similarly, if there are defects in the GPU die due to manufacturing flaws, it can lead to artifacting. The GPU die is the core of the graphics card, and any defects or irregularities can affect its performance and reliability. If this is the case, the GPU may need to be replaced. It’s important to note that if the GPU is still under warranty, the manufacturer should replace it at no additional cost to the user. Both of these issues underline the importance of quality control in the manufacturing process, and the value of a reliable warranty.
Identifying defects
There are a few methods that can be used to detect potential manufacturing defects that could lead to GPU artifacting. A visual inspection of the GPU can serve as the initial step in this process. Carefully examining the GPU for any apparent signs of defects, like broken or burnt components, can offer immediate indications of potential problems.
In addition to visual checks, benchmarking and stress testing the GPU can provide a more thorough evaluation of its performance. Running these tests pushes the GPU to its limits and can help identify any performance issues that might be attributable to manufacturing defects. These inspections and tests are crucial for ensuring the GPU’s functionality and optimal performance, and for preempting any issues that may lead to artifacting.
Wear and tear over time
As with any hardware, aging can play a significant role in GPU performance and stability, potentially leading to artifacting. One issue that can arise over time is the degradation of thermal paste. This paste plays a crucial role in transferring heat between the GPU and its cooling solution. As it degrades, its efficiency in heat transfer decreases, which can lead to GPU overheating. Regular maintenance, such as reapplying thermal paste, can help mitigate this issue and prevent artifacting caused by overheating.
Another issue associated with aging is the wear and tear of components like capacitors. Over time, these capacitors can wear out, leading to instability in the GPU’s performance. This instability can cause artifacting and may require the capacitors to be replaced, a task that typically needs professional assistance, or in some cases, a complete GPU replacement.
General degradation of components over time can also lead to reduced stability of the GPU. This reduction in stability can make the GPU more susceptible to issues, particularly under heavy workloads, thus increasing the potential for artifacting. Regular maintenance and timely upgrades can help manage these aging-related issues and ensure the longevity and performance of the GPU.
Overclocking
Overclocking a GPU to boost its performance is a common practice, but it’s a delicate process that can lead to artifacting if not done correctly. Overclocking involves increasing the core and memory clock speeds of the GPU beyond the manufacturer’s recommended values. While this can potentially enhance performance, it can also cause the GPU to overheat, leading to instability and increased risk of artifacting.
Similarly, increasing the power limit of the GPU can enable higher overclocks, but if pushed too far, it may result in instability due to the excessive heat generated from the GPU working beyond its safe limits. Aggressive overclocking can also strain GPU components, potentially shortening their lifespan.
Another practice associated with overclocking is increasing the GPU voltage to enable higher clock speeds. However, this practice, known as overvolting, can lead to overheating if not managed properly. Excessive voltage can cause permanent damage to the GPU, possibly leading to artifacting or even total hardware failure.
Moreover, modifying the memory and core frequencies of the GPU is a method used to optimize GPU performance. However, improper adjustments can result in instability. The impact of custom frequency control can be a double-edged sword: while it may improve performance, it could also affect the stability and temperature of the GPU, thereby increasing the risk of artifacting.
Insufficient wattage
The Power Supply Unit (PSU) plays a critical role in ensuring the stable operation of a GPU. If a PSU is unable to deliver the necessary power due to insufficient wattage, it can cause instability in the GPU’s performance. An underpowered GPU can lead to overall system instability and even cause crashes.
Additionally, insufficient power can force the GPU to throttle its performance, resulting in lower frame rates and sub-optimal gaming or rendering experiences. This power deficiency can also lead to the GPU struggling to maintain stable performance, potentially resulting in artifacting.
Another concern involves voltage fluctuations often associated with low-quality PSUs. These fluctuations can impact the stability of the GPU, potentially leading to inconsistent performance. A common issue with substandard power supplies is voltage ripple, which can cause inconsistent power delivery, further affecting the GPU’s performance and increasing the risk of artifacting.
Lastly, unstable voltage can result in inconsistent power delivery to the GPU, which can lead to instability and increased likelihood of artifacting. This underscores the importance of investing in a high-quality PSU that can provide stable and consistent power to the GPU, ensuring optimal performance and reducing the risk of issues like artifacting.
Outdated drivers
GPU drivers play an integral role in ensuring smooth operation of games and applications. However, running outdated drivers can lead to several problems. For instance, these older drivers may lack optimizations needed for newer games and applications, resulting in suboptimal performance. They may also contain unresolved bugs that could impact the performance and stability of your GPU, hence the need to update to the latest drivers regularly.
Moreover, installing incorrect drivers intended for a different GPU model can cause instability and even lead to artifacting. Similarly, using beta or unsupported driver versions might introduce bugs or compatibility issues that could compromise the GPU’s performance.
Incompatibility between the GPU and its drivers can also lead to system-wide instability, including crashes and artifacting. This highlights the importance of keeping your GPU drivers updated and ensuring that you’re using the correct drivers for your specific GPU model. Doing so helps optimize GPU performance, reduce the risk of artifacting, and ensure a stable and efficient system performance.
Background Applications
Artifacting occurs when a device is out of power or has several processes running at the same time, causing it to slow down. There are also other variables, such as background applications running and using resources that your game may require. Moreover, if you’re doing multiple tasks on your PC at once while having several apps opened simultaneously, this may be a reason why your GPU isn’t coming up to your expectations. As a consequence, the GPU will not exhibit any BSOD problems, but the visual data will not be displayed in its original form.
How can Artifacting GPU be fixed?
Disabling background apps can also be helpful, but only if you are very certain that no vital apps or services are at risk. Additionally, you may check RAM performance, switch to a lower graphics setting, or close apps as you go. For the time being, you might try the lower settings for the time being to see whether it solves the issue. There are several reasons for GPU artifacts to occur. But how can an Artifacting GPU be fixed? Don’t panic; we have several solutions for your ease.
Conclusion
In this post, we have discussed what is Artifacting GPU in detail and how it affects game performance, especially the graphics output. We hope that our readers will have some knowledge of the artifact and will be able to use it in the future. This also concludes the three most effective ways to fix GPU artifacts. If your GPU is under warranty, you will need to return it to the manufacturer for repair. If your GPU is not covered by the warranty, you will need to replace your graphics card. Consider the power connector used by the card.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes Artifacting in games?
The games are the most affected by GPU Artifacting. Artifacting can cause strange images and other anomalies, as well as black screens and locks, slowdowns, crashes, and long load times. There may be several reasons why GPU certificating is happening. You may haven’t upgraded software or GPU drivers on your device even when an update is available. Artifacting may happen if too many apps are running in the background.
It’s important to close apps and adjust the graphics settings if your gamers wish to prevent Artifacting issues. Upgrading your device can sometimes provide performance benefits. Please check to see if there is a problem with your PC and if the games are running slowly, crashing, or not downloading properly. Close applications and reduce the graphics setting if something seems off to restore power to vital functions.




![How to Fix GPU Sag? [2024]](https://www.ingameloop.com/wp-content/uploads/How-to-Fix-GPU-Sag-450x257.jpg)
![How to update GPU Drivers Windows 11? [Auto & Manual]](https://www.ingameloop.com/wp-content/uploads/How-to-Update-GPU-Drivers-Windows-11-450x257.jpg)
![Does GPU Affect FPS? [2024]](https://www.ingameloop.com/wp-content/uploads/Does-GPU-affect-FPS-450x257.jpg)
